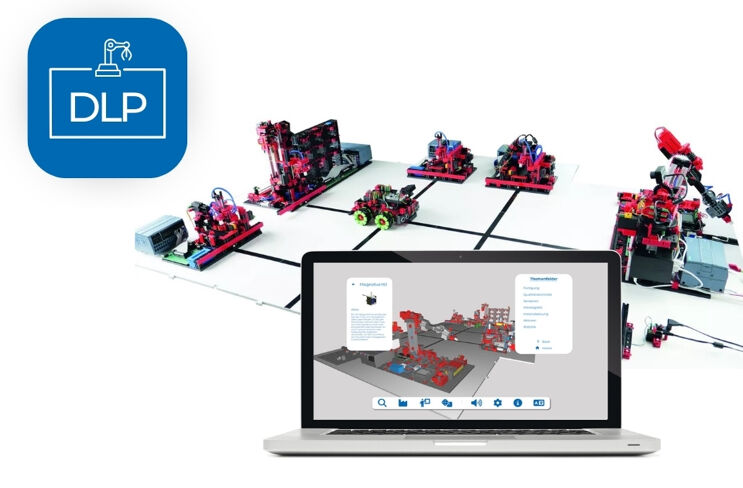
Quality Assurance with AI
In the Quality Assurance module, a vacuum gripper places the workpiece on a conveyor belt. It is transported underneath the camera and scanned there. The workpieces, which come in three different colors (white, red, blue), with three machining features (drilling, milling, drilling & milling), as well as various fault patterns, are classified using the trained AI. Depending on the color, feature and fault pattern, the workpieces are then either placed back onto the AGV as “okay“ or sent to the reject container as “not okay“.